When you get hurt, your body has an amazing way of fixing itself. It’s called the tissue regeneration process, and it’s how your body rebuilds and repairs damaged parts. Understanding this natural healing ability can help us appreciate just how resilient we are. This article will walk you through how this process works, what influences it, and even some ways to help it along.
Key Takeaways
- The tissue regeneration process is your body’s natural way of fixing injuries.
- Several things can impact how well your body heals, like your overall health.
- There are ways to help your body’s natural healing process work better.
What Is the Tissue Regeneration Process?
So, what exactly is tissue regeneration? Well, it’s basically the body’s way of fixing itself after an injury. Think of it as a super-powered repair system that aims to restore damaged tissues to their original state. It’s not just about patching things up; it’s about making them like new again.
Tissue regeneration is the natural process of replacing damaged or lost tissues with new, fully functional ones. This is different from simple wound healing, which might involve scar formation. With true regeneration, the new tissue is identical in structure and function to the original.
How does this work in practice? It’s a complex process involving cell growth, cell differentiation, and tissue remodeling. Different types of tissues have different capacities for regeneration. For example, some animals, like salamanders, can regenerate entire limbs, a feat that regeneration in humans can’t quite match. But even in humans, certain tissues regenerate more readily than others.
The process involves a coordinated series of cellular events, including inflammation, cell proliferation, and matrix remodeling. Growth factors and signaling molecules play a big role, guiding cells to the right place and telling them what to do.
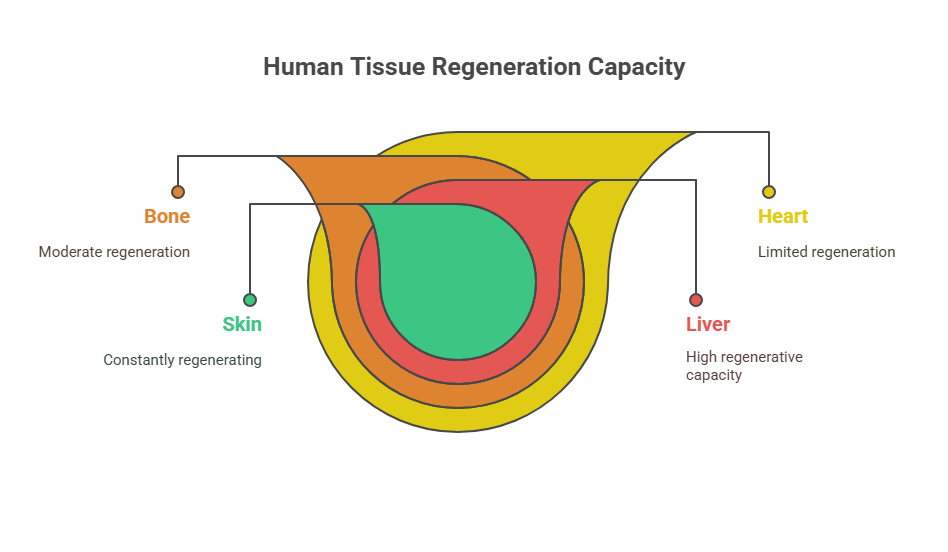
Here’s a quick look at how often do tissues regenerate:
- Skin: Constantly regenerating
- Liver: High regenerative capacity
- Bone: Moderate regenerative capacity
- Heart: Limited regenerative capacity
Understanding the basics of tissue regeneration and repair is key to developing new therapies for injuries and diseases. Researchers are actively exploring ways to boost the body’s natural regenerative abilities to improve healing outcomes. It’s a fascinating field with a lot of potential for future medical breakthroughs. The question of which tissue regenerates well is a hot topic in research, as scientists try to understand why some tissues are better at it than others. The ultimate goal is to harness these natural processes to help people recover from injuries and illnesses more effectively. Tissue regeneration frequency depends largely on both the tissue type and the level of damage sustained.
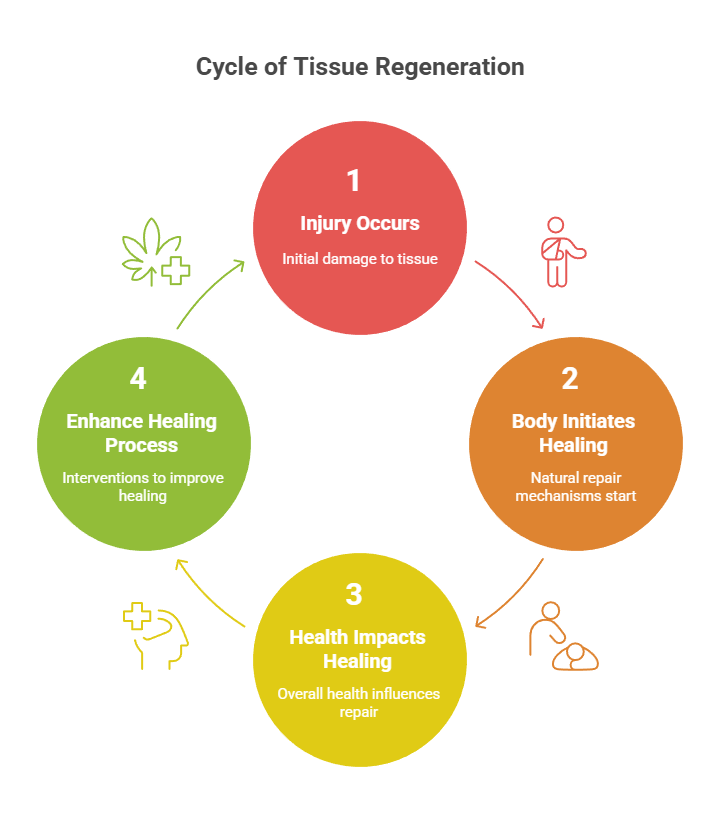
Stages of the Tissue Regeneration Process
Okay, so you’ve got an injury. What happens next? Well, tissue regeneration isn’t just one thing; it’s a series of steps your body takes to patch things up. It’s like a construction project, but instead of bricks and mortar, it’s cells and proteins. Let’s break down the main phases.
Hemostasis
First up is hemostasis. Think of this as the immediate response – stopping the bleeding. When you get a cut, your blood vessels constrict to slow down blood flow. Then, platelets rush to the scene and start forming a clot. It’s like putting a bandage on the wound, but from the inside. This whole process kicks off almost instantly. The cost of regenerative therapy can vary depending on how well this initial stage goes.
Inflammation
Next comes inflammation. Now, inflammation gets a bad rap, but it’s actually a crucial part of healing. During this phase, your body sends white blood cells to the injury site to clear out damaged cells and any bacteria that might cause infection. You’ll notice swelling, redness, heat, and pain – all signs that your body is hard at work cleaning up the mess. It’s like the demolition crew arriving to tear down the damaged structure before rebuilding can begin.
Proliferation
Then we move onto proliferation. This is where the real rebuilding happens. New tissue is formed, made up of collagen and other cells. The wound starts to contract, and new blood vessels develop to supply the tissue with oxygen and nutrients. It’s like the construction crew starting to lay the foundation and build the walls of the new structure. This stage is all about growth and repair.
Maturation
Finally, there’s maturation, also known as remodeling. This is the long-term phase where the new tissue is strengthened and reorganized. Collagen fibers realign, and the wound fully closes. It’s like the finishing touches on the construction project – painting, landscaping, and making sure everything is solid and functional. Depending on the injury’s severity, this phase may last for weeks, months, or even years.
Think of tissue regeneration like fixing a flat tire. First, you stop the air from escaping (hemostasis). Then, you clean the area (inflammation). Next, you patch the hole (proliferation). Finally, you make sure the patch is secure and the tire is properly inflated (maturation).
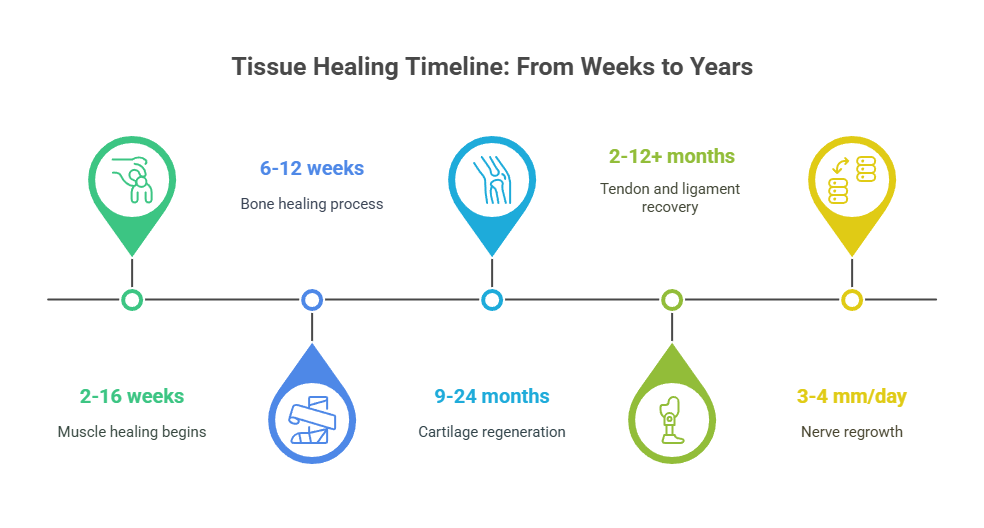
Here’s a quick look at typical healing times for different tissues:
| Tissue Type | Healing Time |
| Muscle | 2-16 weeks |
| Tendon | 2-12+ months |
| Bone | 6-12 weeks |
| Ligaments | 2-12+ months |
| Cartilage | 9-24 months |
| Nerve | 3-4 mm/day (regrowth rate) |
How the Tissue Regeneration Process Supports Healing
The tissue regeneration process is pretty amazing, honestly. It’s how our bodies naturally repair damage, and it plays a huge role in how well we recover from injuries. Think about it: every cut, scrape, or broken bone relies on this process to get you back to normal. It’s not just about patching things up; it’s about rebuilding and restoring function.
The tissue regeneration process is fundamental to healing, promoting the body’s own ability to restore and rebuild injured tissues.
It’s a complex series of events, but the end goal is always the same: to replace injured or dead cells with healthy, new ones. This involves a coordinated effort of different cell types, growth factors, and the extracellular matrix. When it works well, you get complete or near-complete restoration of tissue structure and function. When it doesn’t, you might end up with scar tissue or chronic problems. Understanding how this process works can help us support it and improve healing outcomes. For example, ensuring adequate oxygen for wound healing is crucial.
Factors That Affect the Tissue Regeneration Process
Several things can impact how well your body regenerates tissue. It’s not always a straightforward process, and various factors can either speed things up or slow them down. Understanding these elements is key to supporting your body’s natural healing abilities.
Age
As we get older, our bodies just don’t bounce back as quickly. The rate of tissue regeneration tends to decrease with age. This is because cell turnover slows down, and the body’s ability to repair damage becomes less efficient. It’s a natural part of aging, but it means that older individuals might experience longer healing times compared to younger people.
Nutrition
Nutrition is a key factor in supporting tissue regeneration. Proper healing depends on having the right building blocks for tissue repair. Without key nutrients, the healing process may be delayed or impaired.
- Protein: Crucial for building and repairing tissues.
- Vitamins: Vitamin C, D, and A are important for collagen synthesis and immune function.
- Minerals: Zinc and copper play roles in wound healing.
Vitamins, minerals, and protein in a well-balanced diet are crucial for supporting tissue regeneration. Deficiencies can lead to slower healing and increased risk of complications.
Blood Supply
A nutrient-rich diet supports tissue regeneration by supplying the body with vital building blocks. Without enough blood supply, the cells responsible for regeneration can’t function properly. Disorders that reduce blood circulation, including peripheral neuropathy, can significantly delay healing. Think of it like trying to build a house without a steady supply of materials – it’s just not going to happen.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can interfere with the tissue regeneration process. For instance, diabetes affects blood flow and nerves, complicating the healing of wounds. Autoimmune diseases can also affect the body’s ability to repair itself. These conditions often require careful management to optimize healing outcomes.
Lifestyle Factors
Your daily habits can also impact tissue regeneration. The healing process is hindered by smoking due to its effects on blood vessel constriction and oxygen reduction. Tissue regeneration can be negatively affected by high levels of alcohol intake. Promoting health by exercising regularly and staying away from harmful substances, can support your body’s natural healing abilities. Consider PRP therapy as a way to accelerate healing.
Infection
Infections are a major roadblock to tissue regeneration. When an injury becomes infected, the body’s resources are diverted to fighting the infection, leaving less energy for tissue repair. Infections can also cause further damage to the surrounding tissues, prolonging the healing process. Keeping wounds clean and preventing infection is crucial for optimal regeneration.
Enhancing the Tissue Regeneration Process Naturally
Okay, so you’re looking to give your body a little nudge in the right direction when it comes to healing? Makes sense. There are actually a bunch of things you can do to help your tissues regenerate more effectively. It’s not about magic, but more about providing the right environment and resources for your body to do what it already knows how to do. Let’s explore some options.
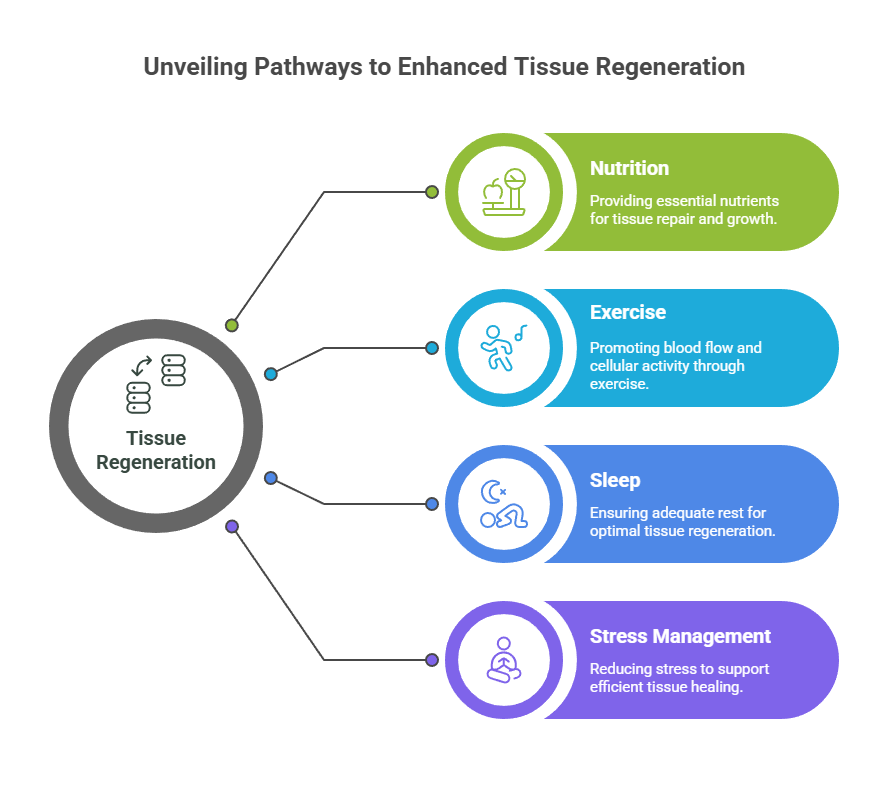
Nutrition’s Role
What you eat seriously impacts how well you heal. Food acts as the foundation your body relies on to heal and rebuild. You need enough protein for tissue repair, vitamins (especially C and D), and minerals like zinc. A balanced diet is key, but sometimes, you might need a little extra help. For example, if you’re dealing with chronic wounds, ensuring adequate nutrient intake is even more critical.
- Protein: Essential for rebuilding tissues.
- Vitamin C: Helps with collagen production.
- Zinc: Important for cell growth and division.
The Power of Movement
Staying active, within your limits, can actually help with tissue regeneration. Light movement helps boost circulation around the injury site, which brings more oxygen and nutrients. Just don’t overdo it! Pay attention to your body and steer clear of activities that cause discomfort. Think of it as a delicate balance – enough movement to stimulate healing, but not so much that you cause further damage. It’s also important to consider how movement mechanics play a role in healing. Repetitive or altered movement patterns may stress injured tissue, delaying healing times.
Sleep and Stress Management
Proper sleep and managing stress are key factors you shouldn’t ignore. When stressed or sleep-deprived, your body produces hormones that can hinder recovery. Ensure you sleep 7-8 hours per night and use healthy methods to reduce stress, like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature. It’s all about creating a calm and supportive environment for your body to repair itself. You can also check out Natural Pain and Regenerative Medical Clinic on social media for more tips.
Getting enough rest and controlling stress positively impact more than general well-being; they’re also crucial for tissue regeneration. When you’re relaxed and well-rested, your body can focus its energy on healing and repair.
Supplements to Consider
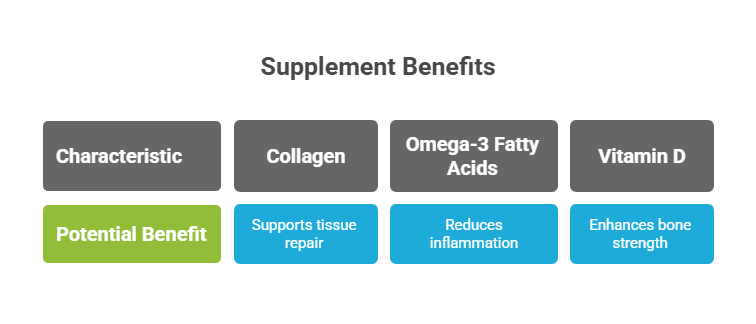
Supplements can complement a balanced diet by offering added nutritional support. Collagen supplements, for example, can provide the raw materials your body needs to rebuild connective tissue. Fish oil provides omega-3s that support inflammation reduction, which can also speed up healing. Before using any new supplements, consult your physician, especially if you have medical conditions or are on treatments.
| Supplement | Potential Benefit |
| Collagen | Supports connective tissue repair |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduces inflammation |
| Vitamin D | Enhances bone strength and boosts immune defenses |
Want to know how your body can heal itself better? Our latest article explains simple ways to help your tissues grow back stronger, all on their own. Learn more about natural healing and how it can help you. Visit our website today to read the full story and discover how to boost your body’s own repair system.
Wrapping Things Up
So, we’ve talked a lot about how our bodies fix themselves after getting hurt. It’s pretty wild to think about, right? From that first moment of injury, your body kicks into gear, doing all these complicated steps to get things back to normal. We looked at how different parts, like muscles or bones, heal up, and how long that can take. But remember, it’s not just about the type of injury; things like your overall health, what you eat, and even how much you move can totally change how fast you get better. Taking care of yourself ahead of time can significantly impact how fast you heal after an injury. It’s all connected.
Frequently Asked Questions

What exactly is tissue regeneration?
Tissue regeneration is your body’s amazing ability to fix itself after getting hurt. It’s like when a lizard regrows its tail, but for us, it’s about repairing skin, muscles, bones, and other parts. This process helps replace damaged cells and tissues with new, healthy ones, making you whole again.
How long does it take for injured tissue to regenerate?
The time it takes for tissue to heal depends on many things, like how bad the injury is, where it is on your body, your overall health, and your age. Minor cuts may heal within days, while broken bones or severe muscle tears can require weeks or months to recover completely. Your doctor can give you a better idea based on your specific injury.
Can I do anything to speed up tissue regeneration?
You can help your body heal better by eating healthy foods, getting enough sleep, avoiding smoking and too much alcohol, and managing stress. Gentle exercise, if allowed by your doctor, can also help blood flow and recovery. Sometimes, special treatments like those offered at places like Waters Edge Medical Clinic & Spa, using things like plasma therapy, can also give your body an extra boost in healing.
If you have any additional questions or if you would like to learn more about regenerative therapies, please contact us at Waters Edge Medical Clinic 727-550-0855.

